A global healthtech provider needed a way to manage software across thousands of smart medical devices spread across clinics with unreliable connectivity. We built a centralized, automated deployment platform that standardized components, automated pipelines, and enabled hands-free updates. The solution ensures reliable rollouts, reduces manual effort, and gives full visibility and control over their distributed fleet. This foundation now supports faster feature delivery and scalable growth across the IoT ecosystem.
The Problem with Updating IoT Devices
Managing software deployments across thousands of distributed IoT devices is one of the most complex operational challenges in any large-scale environment. Every device needs to run the right software version, receive updates automatically, and handle flaky networks without disrupting device functionality.
Our team tackled this challenge for a global healthtech provider operating thousands of smart medical devices across multiple clinical sites. Each device generated event data, such as stock updates, dispense and replace actions, that needed immediate processing and analysis to maintain accurate inventory views.
The client’s existing manual deployment approach couldn’t support a fleet spread across sites with unstable connectivity. They wanted a centralized, automated deployment platform capable of delivering software updates reliably while ensuring security and compliance across all devices.
How We Rebuilt the Deployment Model
We designed an edge-to-cloud architecture that processes data locally while synchronizing with the cloud when available. A centralized automation pipeline handles the entire software lifecycle, from tracking source code changes and building components to securely delivering updates across the fleet. This approach made deployments predictable, scalable, and fully automated, supporting fleet growth without adding operational burden.
Designing the Architecture
We built the platform using AWS IoT Services and Jenkins. The client already used AWS for core systems, which meant we could extend their existing security, identity, and monitoring patterns to the edge without introducing new operational overhead.
AWS IoT Core and AWS IoT Greengrass gave us cloud-to-edge identity management, secure messaging, and a clear model for packaging and deploying components. This allows each device to function autonomously when offline while remaining aligned with system-wide settings.
For the automation layer, we chose Jenkins because it allowed us to design custom pipelines that enforced versioning, packaging standards, and rollout controls. Its integration with AWS services meant we could automate deployments without hardcoding cloud logic into device workflows.
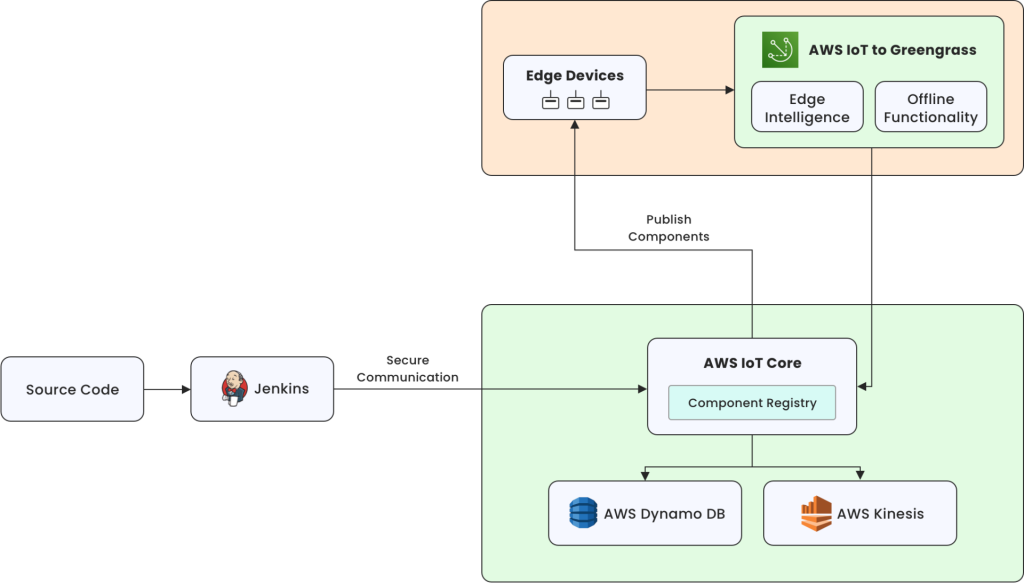
Standardizing Edge Components
A consistent component structure is essential for every Greengrass component, so the automation pipeline can process them without manual adjustments.
Each component follows the same layout with three key files:
- gdk-config.json for build and publish configurations
- recipe.json to define functionality, dependencies, and lifecycle
- deployment.json to specify rollout requirements
This structure allows Jenkins to process all components uniformly, reducing maintenance overhead.
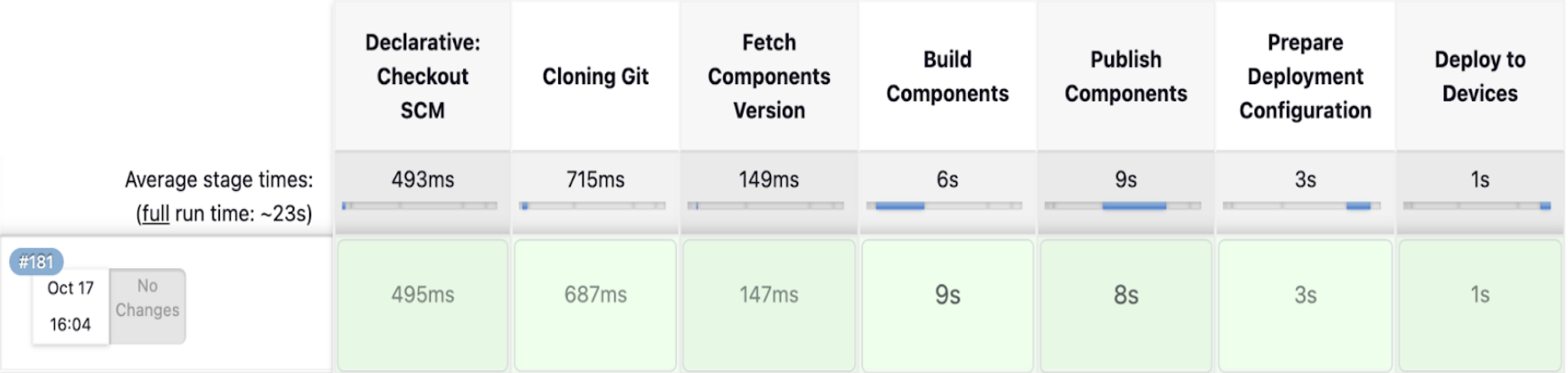
Automating the Full Component Lifecycle
We implemented a Jenkins pipeline that automates the entire journey from source code to device rollout.
The pipeline:
- Retrieves the latest source code from GitHub, using the specified branch or tag.
- Manages versioning by automatically incrementing component versions.
- Builds and packages components using GDK commands to ensure clean, consistent outputs.
- Publishes the components to Amazon S3 and registers them in the Greengrass component registry.
- Deploys the updated components to designated devices or thing groups through the AWS CLI.
This workflow ensures reliable rollouts across distributed edge devices, reduces human error, and accelerates release cycles.
Supporting Tenant-Aware and Environment-Aware Deployments
To meet the client’s operational workflows, we built flexibility directly into the pipelines.
Tenant-Aware Deployments
For multi-tenant deployment scenarios, we implemented isolated pipelines per tenant.
- Each tenant has dedicated configurations, device groups, and deployment workflows.
- Updates could be rolled out safely without impacting others.
- This setup also supports additional device types unique to each tenant, ensuring flexibility in managing diverse hardware requirements.
Environment-Aware Deployments
- Production deployments follow controlled triggers for reliability and compliance.
- Development pipelines are triggered automatically on every code push.
Once components are built and published, Jenkins automatically distributes the appropriate version to the right environment or tenant group. Devices apply updates hands-free, ensuring reliable activation across the fleet.
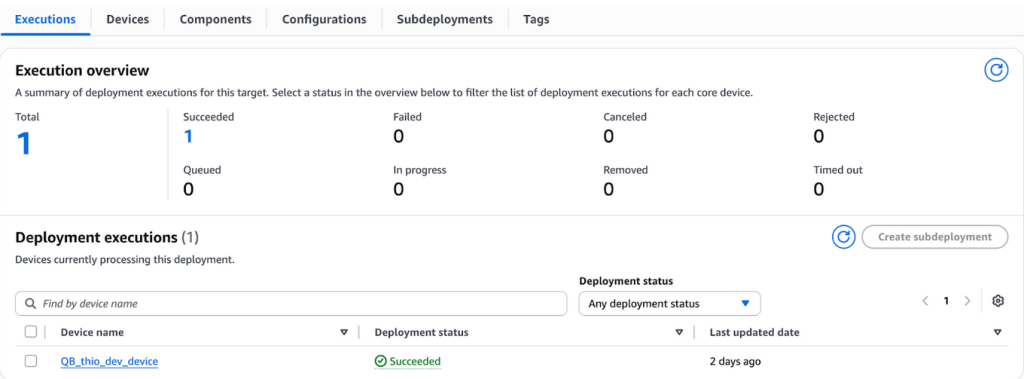
The Implementation Challenges We Addressed
While building the automated deployment platform, one of the major challenges was stabilizing the Greengrass component structure. Small inconsistencies in the component layout or recipe files often caused build failures, so the entire component format had to be standardized to ensure reliable automation.
Another challenge involved the Jenkins pipelines. Early versions of the pipelines faced issues such as branch detection errors, versioning mismatches, and build interruptions due to missing configurations. These required several iterations to refine the pipeline logic and ensure predictable, repeatable executions.
Finally, deployments needed to work across devices with intermittent connectivity. Ensuring that updates are applied reliably, even when devices come online unpredictably, required testing different rollout strategies and validating Greengrass behavior under unstable network conditions.
Addressing these challenges resulted in a more robust and resilient deployment system, designed not only to scale but also to integrate with cloud environments beyond AWS in the future.
How the New Platform Strengthened IoT Operations
By designing and implementing the automated IoT deployment platform, we transformed a manual, error-prone process into a fully streamlined, scalable system. Standardizing component structures, building reliable CI/CD pipelines, automating versioning and rollouts, and integrating edge-aware deployment workflows directly improved operational efficiency.
The new framework drastically reduced effort for updates, eliminated manual intervention across thousands of devices, maintained consistent version control, and ensured reliable rollouts even during intermittent connectivity. End-to-end visibility into deployment status allows faster delivery of new features and fixes, with minimal downtime and improved fleet reliability.
The platform we built now serves as a scalable foundation for future growth. It is designed to accommodate additional device types, support new analytics capabilities, and integrate with cloud environments beyond AWS, ensuring long-term flexibility and adaptability as the client’s IoT ecosystem expands.


